California Department of Food and Agriculture invests in crop-specific research, training for farmers and crop advisors, and development of best practices for nitrogen use.
By Karen Ross, CDFA Secretary
As young students we are taught that water, sunshine, seed and soil are the building blocks of agriculture. Scientists and farmers alike have come to embrace the basic and vital importance of nitrogen as another basic element in farming. It plays an influential role in the growth of our crops, and it is part of a delicate balance in which the goal is to have each plant reach its potential for productivity. The risk of overuse, though, is pollution of our air and water.
The California Nitrogen Assessment, a recent report from UC Davis’ Agricultural Sustainability Institute (ASI), has focused attention on the use of nitrogen on our farms. The report is careful to point out that there are other factors contributing to excess nitrogen in our environment, most notably the burning of fossil fuels. The transportation and energy sectors, wastewater management and other sources are significant as well.
The document acknowledges the use of nitrogen as a building block of plant growth – a vital element in the most basic function of farming. And it confirms that the key to reducing excess nitrogen from the agricultural sector lies in the pursuit of efficient, refined, science-based management of fertilization, irrigation and other farming practices – key priority areas of CDFA’s Fertilizer Research and Education Program (FREP).

FREP-funded UCCE “Pump and Fertilize” trials, 2012-2015.
CDFA’s FREP is dedicated to the scientific pursuit and practical implementation of that science for the efficient use of fertilizers. The program is tailored to the needs of individual crops, soil types, irrigation systems and other factors. In fact, FREP is for just that purpose, and it has been steadily adding to the relevant science for the last 25 years.
Californians – and California farmers – have been given a tremendous gift in the form of our state’s potential for growing good food. That gift comes with a responsibility to be good stewards of the land and all the natural resources that contribute to its suitability and fertility. That stewardship extends beyond and below the land, to the groundwater that many of our farmers must draw from during droughts like the current one, now in its fifth year.
Measuring success in nutrient management is a complex process. As stated in the ASI report, it takes from years to millennia for excess nitrogen from fertilizers to move past the root zone of food crops to reach the groundwater. The challenge of showing progress is further complicated in an environmental system that harbors years of legacy nitrate contamination. But studies like ASI’s 7-year, comprehensive report inform us about our effectiveness in recent years and, more importantly, they confirm that FREP’s work is essential in moving the needle in the right direction. According to the UC Davis Nitrate Report, since the 1970s the gap between synthetic nitrogen applied and harvested has decreased more than 60%.
In the end, reducing that footprint by only giving our crops the nitrogen they can use to produce food – no more, no less – is good for the environment. Fortunately, science has progressed to the point that it is now capable of showing us how to tailor nitrogen use for specific crops, under specific conditions, so that we can get the benefits of nitrogen without the societal or economic costs of excess use.
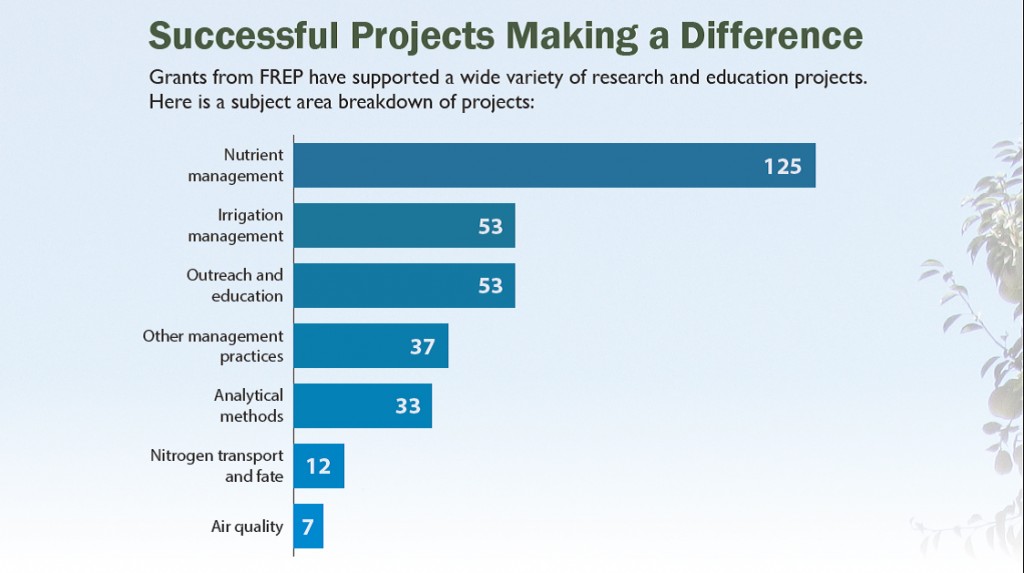 Since its establishment FREP has funded more than 200 research projects, most of them focused on understanding the nitrogen requirements of various crops and developing management practices that improve the performance of nitrogen fertilizers while minimizing their environmental impact. FREP’s most important achievement over the years is the way it makes that research available to the farmers and advisors who are in a position to put it to good use. Examples of FREP’s projects and achievements include:
Since its establishment FREP has funded more than 200 research projects, most of them focused on understanding the nitrogen requirements of various crops and developing management practices that improve the performance of nitrogen fertilizers while minimizing their environmental impact. FREP’s most important achievement over the years is the way it makes that research available to the farmers and advisors who are in a position to put it to good use. Examples of FREP’s projects and achievements include:
California Fertilization Guidelines
Online crop fertilization guidelines provide growers with an important decision-making tool for environmentally safe application of fertilizing materials without compromising crop yield. Growers and advisors have access to information on fertilizer application including how much, when and the best methods. To date, there are nutrient guidelines for 22 crops, representing almost 70% of irrigated acres in California.
These guidelines have been developed through a partnership between CDFA and UC Davis to address the increasing demand from growers and advisors for accurate, timely, efficient and effective crop nutrient information across the state, especially in the San Joaquin Valley’s Tulare Lake Basin and in the Central Coast region’s Salinas Valley. These two regions collectively represent a high degree of nitrogen sensitivity relative to drinking water quality and supplies.
CropManage
Funded by FREP, CropManage is a decision-making tool for growers developed by UC Cooperative Extension. Growers can integrate publically available soil and climate data with in-field measurements to create efficient irrigation and fertilization recommendations. The online tool was developed by Michael Cahn with UC Cooperative Extension and UC ANR, and schedules and tracks water and nitrogen fertilizer applications for growers planted fields. The application is designed to help farmers conserve water and make better use of nitrogen fertilizer while maintaining crop productivity and quality.
Nitrogen Management Training Program for Advisors
Recognizing the need for nitrogen management and training programs for both growers and crop advisors, in 2014 CDFA funded a training program to address these needs. Through this partnership with the University of California Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources (UC ANR), California Association of Pest Control Advisers, and California Certified Crop Advisors, nearly 900 Certified Crop Advisors (CCA) have been trained through 9 one-and-a-half-day sessions. The Nitrogen Management Training Program provides technical and applied information to improve CCAs’ understanding of sound nitrogen management practices and their ability to make informed recommendations to growers.
Nitrogen Management Training for Central Valley Growers
 In another collaborative project, FREP and Coalitions for Urban/Rural Environmental Stewardship (CURES) extended the nitrogen management training to the growers in high vulnerability areas in the Central Valley. This training enables the growers to self-certify their own nitrogen management training required by the regional Water Board. In 2015 and 2016, 31 grower training sessions were held with 28 CCAs trained as lead instructors. This project provided nitrogen management training to more than 1,880 growers.
In another collaborative project, FREP and Coalitions for Urban/Rural Environmental Stewardship (CURES) extended the nitrogen management training to the growers in high vulnerability areas in the Central Valley. This training enables the growers to self-certify their own nitrogen management training required by the regional Water Board. In 2015 and 2016, 31 grower training sessions were held with 28 CCAs trained as lead instructors. This project provided nitrogen management training to more than 1,880 growers.
FREP Funded and Applied Research
For 25 years, the FREP program has been investing in pioneering fertilizer research focused on agronomic efficiency in the management of nutrients, precision irrigation and fertigation practices, soil, crop, and fertilizer interactions. FREP has invested $12 million for over 200 technical, research and education projects.
Irrigation Water to Fertilize Vegetables
Through FREP funding, researchers Smith, Hartz and Cahn have just finished three seasons of field trials that demonstrated that the nitrate in groundwater supplied a substantial portion of the fertilizer requirements for lettuce and broccoli. Water quality regulations in many regions of California now require farmers to report the amount of nitrogen fertilizer that they apply to their fields and the nitrate concentration of their irrigation water. By accounting for the nitrate in irrigation water and using the soil nitrate quick test to monitor soil nitrogen levels, growers may be able to significantly reduce the amount of fertilizer nitrogen they apply to vegetable crops.
















